2015年10月25日 星期日
2015年9月20日 星期日
[C筆記]系統呼叫exec()
作用:在程式中呼叫其他程式來運作,將目前行程交託給下一個程式,exec()將行程交託後,原程式將不再繼續運作。
sample code:
main.c
#include <unistd.h>//exec()的宣告
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>//errno的宣告
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char *my_env[] ={"FOOD=coffee",NULL}; //環境變數name=value 並且用NULL告知程式最後項目
if(execle("./coffee","./coffee","donuts",NULL,my_env)==-1)//如果有找到coffee.exe就會跳去執行coffee.exe
{
fprintf(stderr,"cant run:%s\n",strerror(errno));//strerror(errno)為錯誤訊息種類
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
coffee.c
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
char *w = getenv("EXTRA");
if(!w)
w=getenv("FOOD"); //getenv("FOOD")抓取環境變數的值coffee
if(!w)
w = argv[argc -1];
char *c = getenv("EXTRA");
if(!c)
c= argv[argc -1];//讀取argv[1]
printf("%s with %s\n",c,w);
return 0;
}
補充:1
參照execle("./coffee","./coffee","donuts",NULL,my_env)
argc =2 argv[0] ="./coffee" argv[1]="donuts"
補充:2
exec種類
execl 接受引數串列
execv接受引數陣列
execl p 根據 路徑尋找程式
execl pe 使用環境字串的陣列
補充:3
errno 為錯誤編號
strerror(錯誤編號)回傳字串告知何種錯誤
補充:4
if(execle("./coffee","./coffee","donuts",NULL,my_env)==-1)
系統呼叫出問題時通常回傳-1 (但不總是-1)
執行結果
2015年8月30日 星期日
[C筆記]系統呼叫system()
前言: C語言幾乎仰賴著作業系統,system call 存在於核心,是C與OS溝通 的橋梁。
system()使用範例遇到的問題:
我嘗試了無數次cmd指令 echo %s %s >> reports.log
最後發現在我的%s裡面存在著\n換行字元導致我一直只有echo出前面的%s
剛好fgets這方法尾巴會加上換行字元 以及now()的回傳字串也有
sample code:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
char* now()
{
time_t t;
time(&t);
return asctime(localtime(&t));//結尾會自動加上\n導致echo指令出錯
}
int main()
{
char comment[80];
char cmd[120];
fgets(comment,80,stdin); //fgets結尾會自動加上\n導致echo指令出錯
if(comment[strlen(comment)-1] =='\n')
comment[strlen(comment)-1] ='\0';//將\n用字串結尾取代
char x[strlen(now())];
int i;
for(i=0;i<strlen(now());i++)
{
x[i]= *(now()+i); //*now存在記憶體的實字字串(不能修改)所以先丟到陣列進行修改
}
if(x[strlen(x)-4]=='\n')
x[strlen(x)-4]='\0';
sprintf(cmd,"echo %s %s >> reports.log",x,comment);
system(cmd);
return 0;
}
輸出結果
2015年7月24日 星期五
[java筆記]連結mysql
sample code
public void start(Stage stage) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //jdbc驅動先載入 要加入mysql-connector-java-5.1.15-bin.jar不然會出錯
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=Big5";//我的資料庫url
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","1234");//帳號密碼
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Test.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);//例外處理
}
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement();
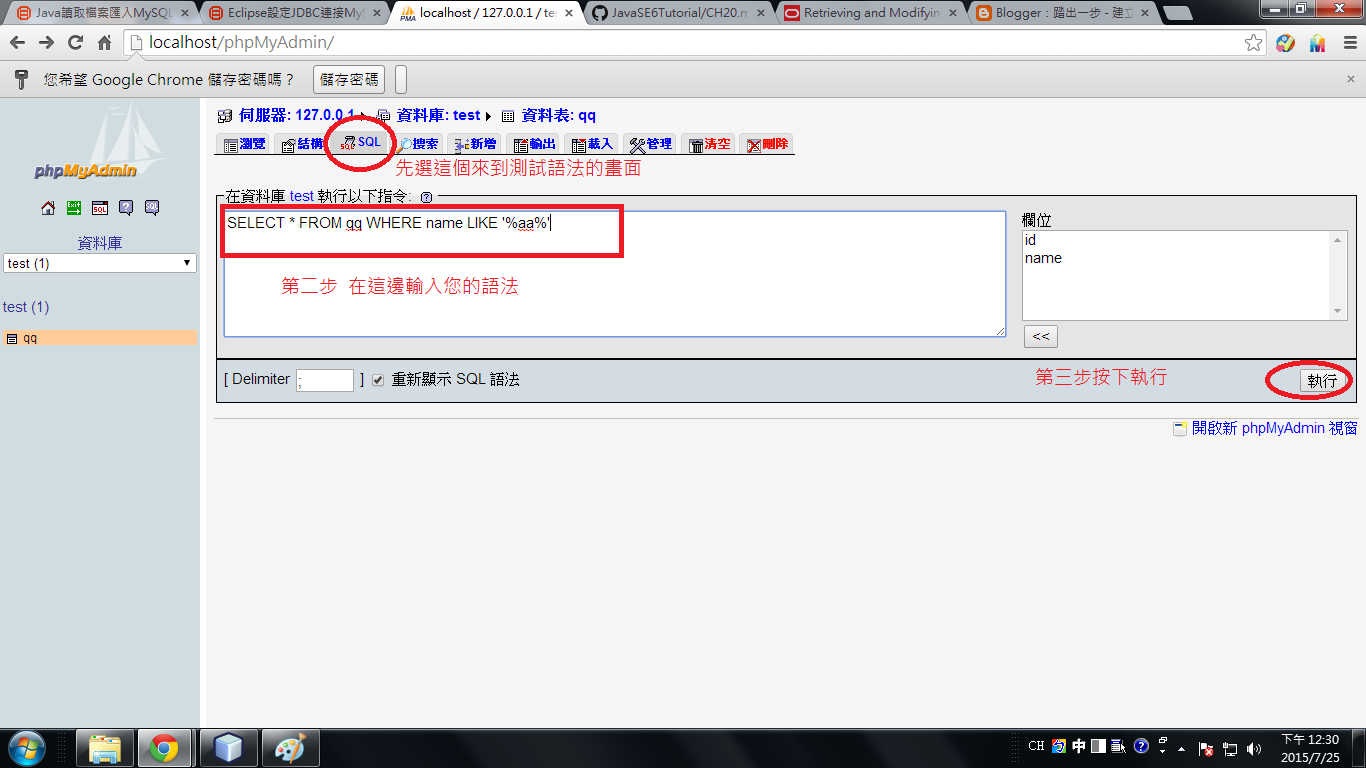
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM qq WHERE name LIKE '%aa%'"); //qq 是資料表名子 name是欄位
while (result.next()) { // ResultSet 為"集合" 一定要配合迴圈使用!
String Name = result.getString("name");//在這裡我找到了2筆一筆內容 aa 另一筆內容 bbaabb
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Test.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}finally {
if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); }//關閉 Statement
}
}
我的資料庫介紹
程式碼執行記錄
我利用中斷點來看每一圈收到的值
第一圈找到 aa!!
另外補充
當妳想確認SQL語法是否正確
可以在http://localhost/phpMyAdmin/ 測試
結果呢(這代表法語法正確)
可以直接回上一頁複製語法
貼近去java 這行裡面
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM qq WHERE name LIKE '%aa%'");
2015年7月19日 星期日
[C筆記]靜態程式庫(共用.h檔與共用.o檔)
前言:之前有提過為了不寫出臃腫不堪的程式碼,我們應該講每個功能(方法)分散寫到不同的.c檔(利用.h檔來共用方法),這裡記錄該如何在gcc下將不同目錄的.h及.o連結到一起!
main.c檔案的位置
checksum.h檔案位置
encrypt.h檔案位置
checksum.o及encrypt.o的位置
main.c code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "encrypt.h"
#include "checksum.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char s[]="speak sumthing";
encrypt(s);
printf("encrypt is %s\n",s);
printf("checksum is %i\n",checksum(s));
encrypt(s);
printf("encrypt is %s\n",s);
printf("checksum is %i\n",checksum(s));
return 0;
}
checksum.c code
#include "checksum.h"
int checksum(char *s)
{
int sum =0;
while(*s)
{
sum= sum +*s;
s++;
}
return sum;
}
encrypt.c code
#include "encrypt.h"
void encrypt(char *s)
{
while(*s)
{
*s=*s^31;
s++;
}
}
-I 告知.h檔的位置(folder folder2 2個位置都存在.h檔)
-o檔直接告知my_object_file/encrypt.o
my_object_file/checksum.o
將.o收集到收藏檔(.a檔)裡面
建立收藏檔指令 ar rcs libfilename.a file1.o file2.o <----要收藏的.o檔
建立.a檔開頭一定要lib
執行gcc main.c -L . -lfilename -o try
-L . <---注意 當收藏檔放在自己的目錄下一定要用-L告知 .當下目錄的意思
此範例用.a檔實作:
題外話在linux底下gcc指令 有關路徑的話必須先加上/
例如-I /folder -L/where
2015年7月11日 星期六
[C筆記]彈性可變式函式
前言:這裡想做一個有彈性函式,彈性的意思是我想要在函式輸入參數的部分,不想限制使用者輸入固定的參數數量,例如 printf("%i%i%i%i%i%i%i%i%i",1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9),這個常用的輸出方法不並沒有限制使用者只能輸出幾個參數。
提醒:
#include <stdarg.h> 使用裡面的
類別 va_list //記錄使用者輸入的所有參數
方法 va_start(ap,args) //告訴程式從哪個參數之後才開始抓
方法 va_arg(ap,int) //拿回使用者的參數 並且必須告知使用者參數的類別方法va_end(ap) //結束參數串列
sample code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void total(int args,char *x, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap,x); //從x 參數之後才開始抓參數
int i;
for(i=0;i<args;i++)
{
printf("%i\n",va_arg(ap,int));
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
total(4,"after_char_*x",4,3,2,1);//不算"after_char_*x",只輸出4個參數
system("PAUSE"); return 0;
}
輸出結果
2015年7月9日 星期四
[C筆記]函式指標陣列配合enum當陣列索引值
前言:函式本身就是指標,這裡利用宣告指標陣列來將函式放進陣列裡,利用迴圈將函式通通跑一遍(優點是程式碼看起來精簡,容易擴充其他函式)。
通常會先去判斷enum item
if(enum item ==??)
{
再決定要帶入哪一個函式 但是這樣寫未免太複雜
}
...
...
...
...
if(enum item ==??)
{
每新增一個函式 就外加一段 if 寫下來造成程式的冗長,容易混亂!!
}
這裡利用下列方法改良!
enum item{AFUNCTION,BFUNCTION,CFUNCTION,DFUNCTION,NEWFUNCTION};
enum可當索引值AFUNCTION=0,BFUNCTION=1,CFUNCTION=2,DFUNCTION=3
response r[] ={{"chou", AFUNCTION},{"yi", BFUNCTION},{"ming", CFUNCTION},{"pig",DFUNCTION},{"new", NEWFUNCTION}};
function[r[i].type](r[i]); //這行不變
smaple code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum item{AFUNCTION,BFUNCTION,CFUNCTION,DFUNCTION};
//enum 設定 symbol AFUNCTION=0,BFUNCTION=1,CFUNCTION=2,DFUNCTION=3
typedef struct{
char *name;
enum item type;
}response;
void afunction(response r)
{
printf("%s\n",r.name);
}
void bfunction(response r)
{
printf("%s\n",r.name);
}
void cfunction(response r)
{
printf("%s\n",r.name);
}
void dfunction(response r)
{
printf("%s\n",r.name);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
response r[] ={{"chou",AFUNCTION},{"yi",BFUNCTION},{"ming",CFUNCTION},{"pig",DFUNCTION}};
void (*function[])(response) ={afunction,bfunction,cfunction,dfunction};
//將函釋放入 函式指標陣列裡!
int i;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
function[r[i].type](r[i]);
}
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
執行結果:
2015年7月5日 星期日
[C筆記]函式進階應用講解
前言:一般函式的用法函式(參數) 但是這裡式使用進階用法函式(函式)這種 方式在c函式庫裡常常看到例如qsort(void* array ,size_t array,size_t item, int (*compar) (const void*,const void*))。
提醒:c語言中,函式在宣告的時候就已經是指標位置了,所以我們不存在 Funtion *x 這種宣告,因為函式回傳值沒有固定的類別,帶入的參數也沒有。
???? aa ( ???????)
{
return ?????????;
}
提醒2:如何建造函式的指標呢??
假設有一個函式
int i_am_a_function (int a, char* b)//函數宣告本身就是一個指標位置
{
..............................................
}
我想宣告一個指標取代這個函式
int (*replace) (int, char*);
replace = i_am_a_function;
replace(2,"sucessful"); 等同於 i_am_a_function(2,"sucessful");
qsort 函式(函式) sample code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int compare_scores(const void*,const void*);
int compare_str(const void* ,const void* );
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int scores [] ={543,323,32,554,11,3,112};
qsort(scores,7,sizeof(int),compare_scores);
int i ;
for(i =0; i< sizeof(scores)/4;i++)
{
printf("%i\n",scores[i]);
}
char *name []={"chou","yi","ming","is","pig"};
qsort(name,sizeof(name)/4,sizeof(char*),compare_str);
for(i=0;i<sizeof(name)/4;i++)
{
printf("%s\n",name[i]);
}
return 0;
}
int compare_scores(const void* x,const void* y)
{
int a = *(int*)x;
int b = *(int*)y;
return a-b;
}
int compare_str(const void* stra ,const void* strb)
{
char** a =(char**)stra; // 補充 void* 型別轉回 (char*)* = 字串*
char** b =(char**)strb;
return strcmp(*a,*b);
}
這邊char**不是字串陣列
圖解
這是一個排序程式
輸出結果
2015年7月1日 星期三
[C筆記] 資料結構(Linklist)與動態記憶體Heap配置使用與釋放
前言:為了能夠動態配製記憶體,利用 malloc()來跟記憶體申請空間(HEAP),HEAP空間不像STACK空間會自己釋放掉,所以必須依靠free() 來釋放記憶體。
code sample:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> // 為了使用strdup
typedef struct island//<-命名 island 資料結構為linklist
{
char *name;
char *open;
char *close;
struct island *next ; //遞回結構不能取消"命名"
}island;//<-別名
island* creat(char* name)
{
island *i = malloc(sizeof(island));
i->name = strdup(name); //請憶體配置name複本空間
i->open = "09:00";
i->close = "17:00";
i->next = NULL;
return i;
}
void display(island *start)
{
island *i = start;
for(;i!=NULL;i=i->next)
{
printf("name:%s open:%s - %s\n", i->name,i->open,i->close);
}
}
void release(island *start)
{
island *i = start;
island *next = NULL;
for(;i!=NULL;i=next)
{
next = i->next;
free(i->name);
free(i);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
island *start = NULL;
island *i = NULL;
island *next = NULL;
char name[80];
int count =0;
for(;scanf("%79[^,],[\n]\n",name)== 1;i = next)
{
next =creat(name);
if(start == NULL)
start = next;
if(i != NULL)
i->next = next;
}
display(start);
release(start);
return 0;
}
main解說: 每新增一坐島嶼,就必須動態向記憶體申請一塊Heap空間(因為不知道有幾座島所以無法是先宣告在stack空間裡),建立島嶼的方法中 island* creat(char* name),藍色的兩行都是會向記憶體申請heap。
為什麼要用到strdup呢??原因在於
island* creat(char* name) c語言中不管設定指標或者陣列帶入函式都是送記憶體位置過去(就是指標)
island* creat(char* name) == island* creat(char name[])
換句話說當我們程式碼如果寫這樣 i->name = strdup(name); 紅色部分去除
islandA = creat(name);//假設name內容為a
islandB = creat(name);//假設name內容為b
此時 islandA 與 islandB 中的name 都會被修改成"b" 因為2者name都是指標指向真實記憶體位置
所以用strdup()在記憶體中另行存一個空間(heap),當不需要使用時,當然也必須做釋放的動作。
一個好的工程師除了程式不寫的臃腫不堪外,應該對記憶體的使用在腦海中有相當程度的對應圖。
trip.txt
輸出結果
2015年6月29日 星期一
[C筆記]struct union enum 實作
介紹
struct : 使用者變數不會只是簡單的 int or char 所以用結構來定義使用者所 需要的變數
enum:列舉 讓使用者只能輸入固定值(例如星期幾)(使用實不必加""字串符號)
union: 當使用者需要一個不是特定的單位時候就必須使用union
範例中
typedef union{short count;
float weight;
float volume;
}quantity;
使用者用到"量單位的變數" 可能是整數或者浮點數,就需要使用union ,原因是如果用 struct來做就會造成空間的浪費,必須浪費一個short (2byte)和2個 float (4byte)的記憶體空間來存一個值 ,union 則是以最大空間來變通 float (4byte) 可以省下許多記憶體空間。
sample code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum{count,pounds,pints}unit; // 與struct不同 用,隔開
typedef union{ // quantity x ={5};會被設定第一個欄位 //指定設定 quantity x ={.volume=1.5}; short count;
float weight;
float volume;
}quantity;
typedef struct {
const char *name;
const char *color;
quantity amount;
unit units;
}fruit;
void display(fruit x); //因為有fruit 所以必須放在 typedef struct fruit 下面
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
fruit apple = {"apples","red",.amount.count=150,count}; //不允許先宣告 下一行才設定值 !! apple ={}會被編譯器誤以為陣列
fruit strawberries = {"strawberries","pink",.amount.weight =1.5,pounds};
fruit noisy ={"noisy","nocolor",.amount.volume =1.3,pints};
display(apple);
display(strawberries);
display(noisy);
return 0;
}
void display(fruit x)//如果是改值請用指標改記憶體內的值(這方法純輸出來看所以不帶入指標)
{
if(x.units == count)
printf("%s is %s and %i\n",x.name,x.color,x.amount.count);
else if(x.units == pounds )
printf("%s is %s and %1.1f\n",x.name,x.color,x.amount.weight);
else
printf("%s is %s and %1.1f\n",x.name,x.color,x.amount.volume);
}
輸出結果
2015年6月24日 星期三
[C筆記] typedef struct 觀念 用法
前言:變數不會只侷限在簡單的整數或者字串,撰寫時可以用struct 來做出你想要的類別,C中的類別與其他語言有些不同,struct中不能寫方法只能宣告物件內容。
code: sample
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct
{
const char *descrption;
float value;
} swag;
typedef struct
{
swag *swag ;
const char *sequence;
}combin;
typedef struct
{
combin numbers;
const char *make;
}safe;
void method (safe *safe_pointer)
{
printf("%0.2f\n",safe_pointer->numbers.swag->value);
}
void method2 (safe safe_pointer)
{
safe_pointer.numbers.swag->value =safe_pointer.numbers.swag->value +1;
printf("%0.2f\n",safe_pointer.numbers.swag->value);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
swag gold ={"gold",10.0};
combin numbers ={&gold,"1234"};
safe s ={numbers,"5678"};
method2(s);
method(&s);
return 0;
}
輸出結果:
11.00
11.00
補充說明
method2(s);
編譯器複製了一份一樣架構的資料丟進這個方法裡做一個safe_pointer.numbers.swag->value=safe_pointer.numbers.swag->value+1的運算,在這個方法裡struct做任何的修改都只式改複製版本的值,但是為什麼最後結果會讓 method(&s);輸出也變11呢??
原因是因為雖然是複製版本,但是複製版本的swag欄位為一個指標,他與非複製版本同時指向參數真正儲存記憶體的位置。
method(&s);
編譯器將s在記憶體中的位置資料丟進這個方法裡,在這個方法裡改任何struct中的變數,就是真實在改main中s的資料,
2015年6月23日 星期二
[C筆記]Makefile介紹與實際操作
前言:當我們有一個由多個程式組合而成的一之程式,正常情況下我們修改某個子程式,編譯器執行前必須將每個子程式都在重編譯一次,這非常浪費時間,Makefile可以去幫我們檢查相依關係,並且去檢查修改時間加以判斷哪些子程式需要重編譯,不必花費多餘時間在編譯沒有改動過的子程式上。
實作:
main.cencrypt.c
encrypt.h 內容
void encrypt(char* msg);
關係圖:
補充:利用.c檔 的開頭擋來排出關係圖 ,.c檔經過-c(compile)生出目地擋.o
Makefile檔
encrypt.o: encrypt.h encrypt.c //encrypt.o與 encrypt.h encrypt.c相依
gcc -c encrypt.c
main.o: main.c encrypt.h //main.o 與main.c encrypt.h相依
gcc -c main.c
try: main.o encrypt.o //try.exe 與 main.o encrypt.o相依
gcc main.o encrypt.o -o try
實際操作:假設我修改了encrypt.c 的情況下執行(window指令為mingw32-make)mingw32-make try (linux 下指令為make)
因為我只修改了encrypt.c 所以make只幫我重新編譯encrypt.c (不去編譯main.c !!)
然後再重新Link main.o encrypt.o 來輸出一份try.exe
ref:深入淺出C
2015年6月22日 星期一
[C筆記]利用標頭檔共享程式碼
前言:當有兩個以上的程式檔需要用到某個方法,直觀作法是在兩支程式內都寫下此方法的程式碼,但如果這個共同的方法需要改良,那不就代表我們必須去每支擁有這程式碼的程式都改一遍,這是一件麻煩的事情,這裡利用標頭擋來讓N個程式檔都可以共享一個方法的檔案,只要修改此檔案就可以讓所以引用此方法的程式碼都跟著改變。
範例:
解說:
encrypt.h :用來連結的標頭擋
void encrypt(char *message);//類似宣告方法的回傳值
encrypt.c :想共用方法
#include "encrypt.h" //這邊要將連結用的標頭擋包含進來
void encrypt(char *message)
{
while(*message)
{
*message = *message^31;
message++;
}
}
main.c :主程式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "encrypt.h"//這邊就是共享 encrypt.c 裡面方法的關鍵int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char msg[80];
while(fgets(msg,80,stdin))
{
encrypt(msg);
printf("%s",msg);
}
system("PAUSE"); return 0;
}
最後執行要記的兩個檔一起編譯進去 gcc main.c encrypt.c -o try
補充:當encrypt方法需要修改就直接去改encrypt.c裡面就ok了
2015年6月21日 星期日
[C筆記]命令列選項與命令列引數
practice
sample code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *delivery ="";
int thick =0;
int count =0;
char ch;
while( (ch =getopt(argc,argv,"d:g:t"))!=EOF)
switch (ch){
case 'd':
delivery = optarg;
break;
case 'g':
printf("%s\n",optarg);
case 't':
thick = 1;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unknow option: '%s'\n",optarg) ;
return 1;
}
argc-=optind;
argv+=optind;
if(thick)
puts("thick crust");
if(delivery[0])
printf("to be delivery %s .\n",delivery);
for(count = 0;count<argc;count++)
puts(argv[count]);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
要點補充說明:
getopt 使用前必須先#include<unistd.h>
利用getopt 來設置選項 d : 代表此選項後面必須帶參數(-d now)
命令(try.exe -d now -g go -t output1 output2)
*argc為8
*argv為8 (argv[0]~argv[7])
*變數 optind為6 (output1,output2為參數所以不算命令數)
*變數 optarg 內容利用case '指令' 來區分輸入的參數( case 'd': optarg 為 -d 後面帶入的值)
*arg+=optind (將 arg[0]變成output1 arg[2]變成 output2)
2015年6月20日 星期六
[C筆記]自定資料串流(將輸出到多個檔案)
前言: 作業系統只提供3種資料串流 stdin 、stdout、stderr(標準輸入 標準輸出 標準錯誤),當我們需要更多的輸出、輸入時,可以透過fopen 來定義自己要的資料串流。
重點整理
* fopen 回傳是檔案的指標
FILE * in_file = fopen("input.txt","r"); //r唯讀
FILE *out_file = fopen("output.txt","w"); //w//唯寫
* FILE這個類別一定要大寫(早期巨集定義)
*一個程式最多256個資料串流(視作業系統而定)使用玩季的關閉fclose();
sample code:
輸入
輸出1
輸出2
輸出3
[C筆記] 不去更改已寫好的project 利用管線來解決
前言: 第一之程式工具可以將輸入的資料(經度,緯度)轉換成json格式,此範例如果想要加條件來過濾出我們所要的坐標,最直觀的方法就是在程式碼中加if 條件來過濾,但是這個方法並不是一個好方法(因為必須去動到別人已寫好的工具),長期這樣改下來這隻程式反而會有太多多餘不必要的code出現,因此用管線的方式來取代上數的過濾條件。
C code 1: 將輸入的資料轉換成Json格式
Code 1編譯出 Map.exe 檔
C code 2: 過濾出我們要的位置
Code 2 編譯出 Range.exe 檔
(注: | 為管線 aa.txt檔案餵給Range.exe 過濾出我們要的坐標後再透過管線直接餵給map.exe最後將結果存到bb.json
結果:
aa.txt
bb.json
注過濾出來的結果
[C筆記] 將資料透過小工具轉換格式輸出
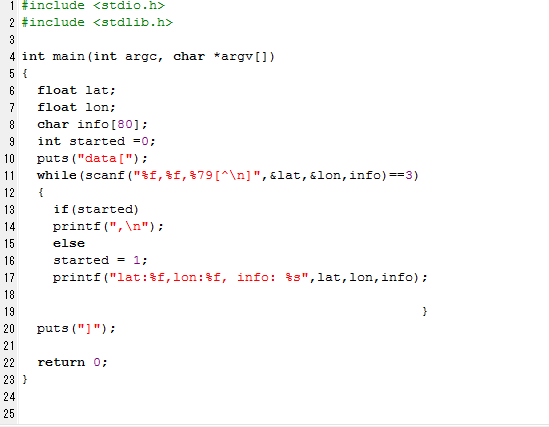
前言: C語言程式在比較實用的情況下往往需要將資料以檔案的形式輸出,並將此檔案餵給其他小工具,此範例將我們所需要的資料內容轉換成JSON格式輸出。
C :code
gcc main.c -o trycode
C :code
Input : aa.txt
輸入不再是手動輸入,而是透過指令將檔案直接餵給程式
gcc main.c -o trycode
在windows底下 trycode必須加.exe
trycode.exe < aa.txt > bb.txt ( <輸入 >輸出)
output : bb.txt
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)